The global burden of cancer is predicted to rise to nearly 22 million cases and 13 million deaths by 2030, with the major burden on low and middle-income countries.
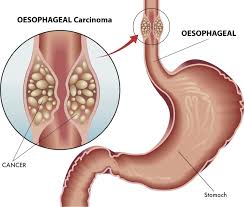
Today, we focused on esophageal cancer, a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the esophagus.
It is a type of cancer where the growth of cells starts in the esophagus, also known as the food pipe, which is a tube that connects the throat to the stomach and takes food slowly down the throat into the stomach.
The esophagus is part of the digestive system and is responsible for moving food from the throat to the stomach.
Dr. Wilberforce Kabweru, a senior consultant surgeon at Mulago National Referral Hospital, says that esophageal cancer occurs when cells in the esophagus grow and multiply uncontrollably, forming a tumor.
He adds that esophageal cancer is a serious health condition that ranks among the top five dangerous cancers in the country, it affects more blacks than whites across all ages, unlike like in the past when it was believed to be cancer of the elderly.
“The tables have turned around from the narrative that it is among the elderly; now it happens to people in their 40’s, 30’s, 20’s, and even teens,” Dr. Kabweru said.
How can one detect esophageal cancer?
According to Dr. Kabweru, once one experiences dysphagia (difficulties in swallowing), where one used to swallow solid foods easily and can no longer do so, then turned to soft foods, before resorting to drinks only, and finally even swallowing their own saliva, this is a common problem, including weight loss due to failure to eat normally, chest pain, hoarseness, and coughing.
However, he notes that understanding the cause, symptoms, and treatment options for this type of cancer is crucial for early detection and effective management.
“People at high risk of esophageal cancer are heavy alcohol users, chronic acid reflux, excess weight, smoking, and diets low in fruits and vegetables and high in processed foods,” Dr. Kabweru said.
Dr. Kabweru explained that, once healthcare providers suspect esophageal cancer, a number of treatment options may be used depending on the stage of the disease, the location and size of the tumor, and the overall health of the patient.
“The disease may spread to the lungs, causing chest pain; to the brain, causing headaches; and to the bones, causing upper back pain,” Dr. Kabweru adds.
The common treatment options, according to Dr. Kabweru, include surgery (removal of the affected portion of the esophagus known as an esophagectomy), normally done during the early stage of esophageal cancer.
Other ways are radiation therapy (where high radiation energy is used to destroy the cancer cells and shrink the tumor) and chemotherapy: drugs that kill rapidly dividing cancer cells are administered through intravenous and palliative care for advanced-stage esophagus cancer.
Dr. Kabweru says early-stage esophagus cancer has a better prognosis because esophagus cancer is an aggressive form of cancer, and early detection is critical for improving outcomes and survival rates.